Genomic analyses of the
transcription elongation factor Spt5
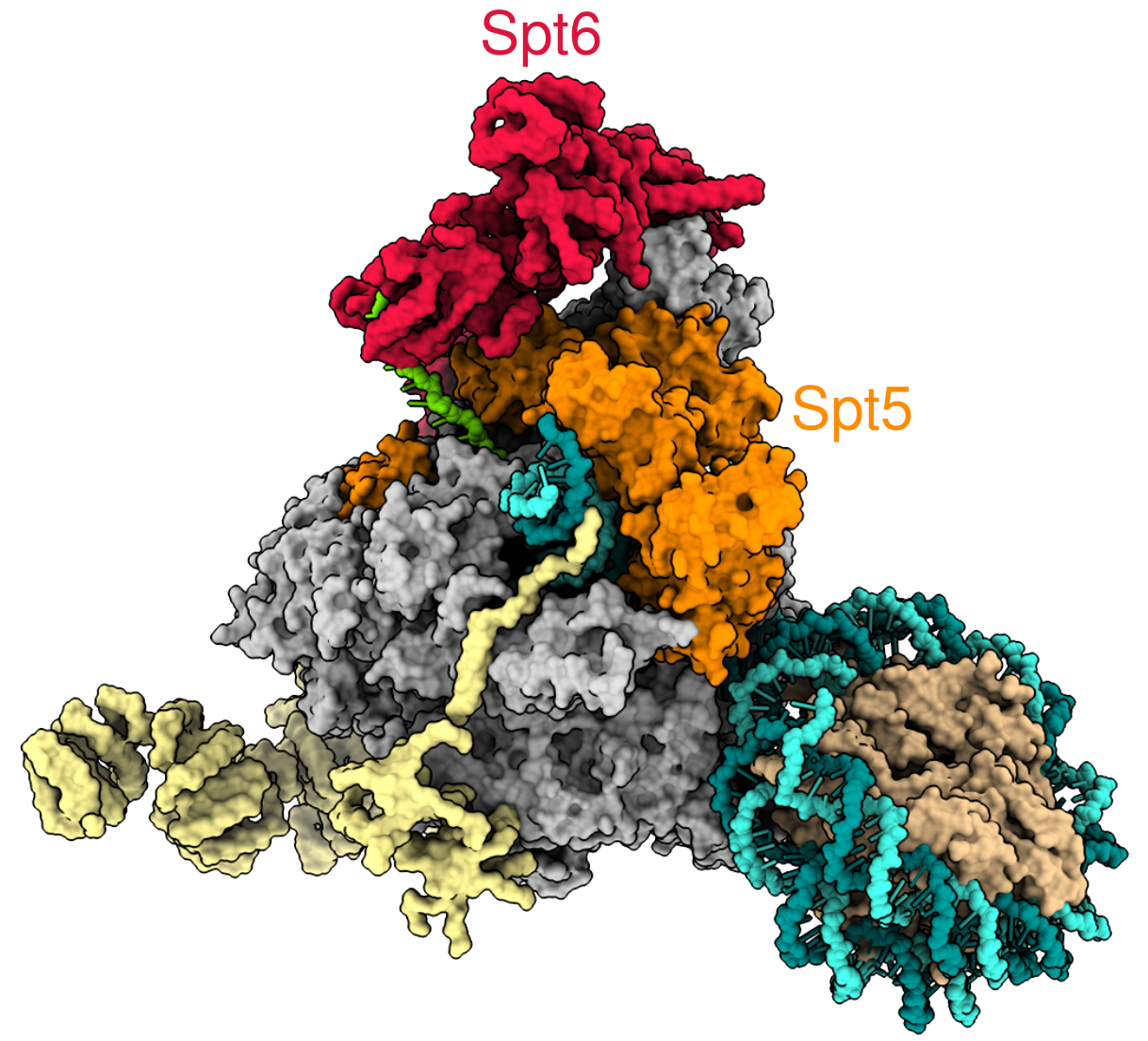
As a graduate student/postdoc in the Fred Winston lab, I did data science work on a project studying the conserved transcription elongation factor Spt5.
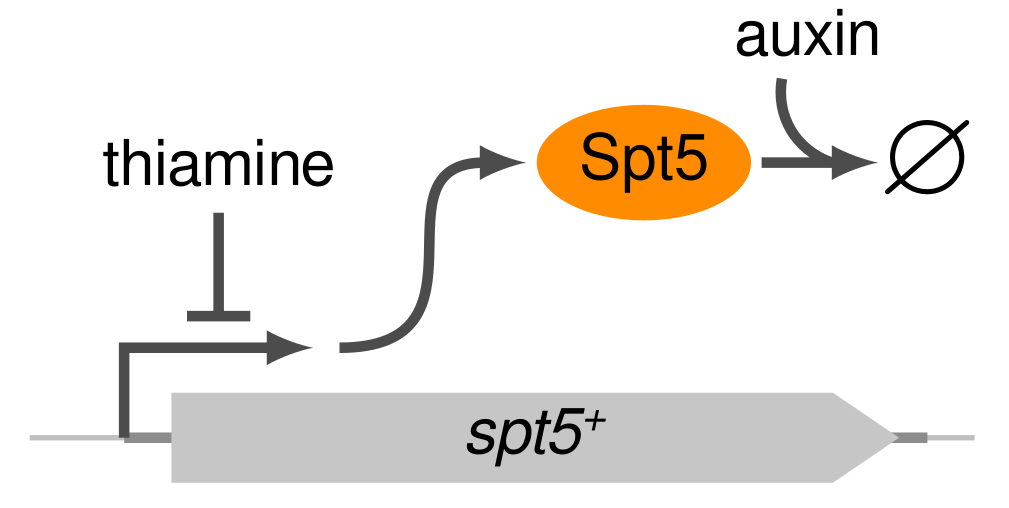
In this project, I analyzed multiomics data collected by a collaborator in the lab from Schizosacchomyces pombe cells that have been depleted of Spt5 protein.
This work appears in chapter 3 of my PhD dissertation, and extends upon results published in Shetty et al. (2017) that showed in vivo transcriptional elongation defects upon Spt5 depletion and a novel role for Spt5 in regulating antisense transcription.